We now have 20 new members of the College of Cardinals. Men who come from various parts of the world. 15 of the 20 are able to vote in a future conclave, and the 5 are honorary due to age. (Over the age of 80 a cardinal does not enter the conclave to elect a new Roman Pontiff.) The novelty in this group of cardinals is that several dioceses receive for the first time: there are 5 firsts: Agrigento (Sicily), Morelia (Mexico), David (Panama), Santiago de Cabo Verde (Cape Verde), Tonga (Kingdom of Tonga).
We now have 20 new members of the College of Cardinals. Men who come from various parts of the world. 15 of the 20 are able to vote in a future conclave, and the 5 are honorary due to age. (Over the age of 80 a cardinal does not enter the conclave to elect a new Roman Pontiff.) The novelty in this group of cardinals is that several dioceses receive for the first time: there are 5 firsts: Agrigento (Sicily), Morelia (Mexico), David (Panama), Santiago de Cabo Verde (Cape Verde), Tonga (Kingdom of Tonga).
One of the cardinals that catches my eye is His Eminence, Berhaneyesus Demerew Cardinal Souraphiel, CM, 66, archbishop of Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Cardinal Souraphiel comes from a country where Catholics number less than 1 percent of a total population and the majority are Orthodox Christian; more than 30 percent are Muslim. He also brings the Vincentian charism to the College of Cardinals.
The youngest cardinal at the age of 53 is Soane Patita Paini Mafi, bishop of Tonga, a diocese with about 15,000 Catholics. Part of his education was in the USA having spent two years in Baltimore studying psychology before returning home for parish and seminary assignments. Pope Benedict XVI named him bishop in 2007.
One of the honorary cardinals, His Eminence, Luigi Cardinal De Magistris, 88, Major Pro-Penitentiary Emeritus, is noteworthy and well-deserving.
“The greater our responsibility in serving the Church, the more our hearts have to expand according to the measure of the heart of Christ. It means being able to love without measure, but also to be faithful in particular situations and with practical gestures.”
Pope Francis told the new cardinals (but what the Pope says is applicable to all):
The cardinalate is certainly an honour, but it is not honorific. This we already know from its name – “cardinal” – from the word “cardo”, a hinge. As such it is not a kind of accessory, a decoration, like an honorary title. Rather, it is a pivot, a point of support and movement essential for the life of the community. You are “hinges” and are “incardinated” in the Church of Rome, which “presides over the entire assembly of charity” (Lumen Gentium, 13; cf. IGN. ANT., Ad Rom., Prologue).
In the Church, all “presiding” flows from charity, must be exercised in charity, and is ordered towards charity. Here too the Church of Rome exercises an exemplary role. Just as she presides in charity, so too each particular Church is called, within its own sphere, to preside in charity.
For this reason, I believe that the “hymn to charity” in Saint Paul’s first letter to the Corinthians can be taken as a guiding theme for this celebration and for your ministry, especially for those of you who today enter the College of Cardinals. All of us, myself first and each of you with me, would do well to let ourselves be guided by the inspired words of the apostle Paul, especially in the passage where he lists the marks of charity. May our Mother Mary help us to listen. She gave the world Jesus, charity incarnate, who is “the more excellent Way” (cf. 1 Cor 12:31); may she help us to receive this Word and always to advance on this Way. May she assist us by her humility and maternal tenderness, because charity, as God’s gift, grows wherever humility and tenderness are found.
Saint Paul tells us that charity is, above all, “patient” and “kind”. The greater our responsibility in serving the Church, the more our hearts must expand according to the measure of the heart of Christ. “Patience” – “forbearance” – is in some sense synonymous with catholicity. It means being able to love without limits, but also to be faithful in particular situations and with practical gestures. It means loving what is great without neglecting what is small; loving the little things within the horizon of the great things, since “non coerceri a maximo, contineri tamen a minimo divinum est”. To know how to love through acts of kindness. “Kindness” – benevolence –means the firm and persevering intention to always will the good of others, even those unfriendly to us.
The Apostle goes on to say that charity “is not jealous or boastful, it is not puffed up with pride”. This is surely a miracle of love, since we humans – all of us, at every stage of our lives – are inclined to jealousy and pride, since our nature is wounded by sin. Nor are Church dignitaries immune from this temptation. But for this very reason, dear brothers, the divine power of love, which transforms hearts, can be all the more evident in us, so that it is no longer you who live, but rather Christ who lives in you. And Jesus is love to the fullest.
Saint Paul then tells us that charity “is not arrogant or rude, it does not insist on its own way”. These two characteristics show that those who abide in charity are not self-centred. The self-centred inevitably become disrespectful; very often they do not even notice this, since “respect” is precisely the ability to acknowledge others, to acknowledge their dignity, their condition, their needs. The self-centred person inevitably seeks his own interests; he thinks this is normal, even necessary. Those “interests” can even be cloaked in noble appearances, but underlying them all is always “self-interest”. Charity, however, makes us draw back from the centre in order to set ourselves in the real centre, which is Christ alone. Then, and only then, can we be persons who are respectful and attentive to the good of others.
Charity, Saint Paul says, “is not irritable, it is not resentful”. Pastors close to their people have plenty of opportunities to be irritable, to feel anger. Perhaps we risk being all the more irritable in relationships with our confreres, since in effect we have less excuses. Even here, charity, and charity alone, frees us. It frees us from the risk of reacting impulsively, of saying or doing the wrong thing; above all it frees us from the mortal danger of pent-up anger, of that smouldering anger which makes us brood over wrongs we have received. No. This is unacceptable in a man of the Church. Even if a momentary outburst is forgivable, this is not the case with rancour. God save us from that!
Charity – Saint Paul adds – “does not rejoice at the wrong, but rejoices in the right”. Those called to the service of governance in the Church need to have a strong sense of justice, so that any form of injustice becomes unacceptable, even those which might bring gain to himself or to the Church. At the same time, he must “rejoice in the right”. What a beautiful phrase! The man of God is someone captivated by truth, one who encounters it fully in the word and flesh of Jesus Christ, the inexhaustible source of our joy. May the people of God always see in us a firm condemnation of injustice and joyful service to the truth.
Finally, “love bears all things, believes all things, hopes all things, endures all things”. Here, in four words, is a spiritual and pastoral programme of life. The love of Christ, poured into our hearts by the Holy Spirit, enables us to live like this, to be like this: as persons always ready to forgive; always ready to trust, because we are full of faith in God; always ready to inspire hope, because we ourselves are full of hope in God; persons ready to bear patiently every situation and each of our brothers and sisters, in union with Christ, who bore with love the burden of our sins.
Dear brothers, this comes to us not from ourselves, but from God. God is love and he accomplishes all this in us if only we prove docile to the working of his Holy Spirit. This, then, is how we are to be: “incardinated” and docile. The more we are “incardinated” in the Church of Rome, the more we should become docile to the Spirit, so that charity can give form and meaning to all that we are and all that we do. Incardinated in the Church which presides in charity, docile to the Holy Spirit who pours into our hearts the love of God (cf. Rom 5:5). Amen.
Saturday, 14 February 2015
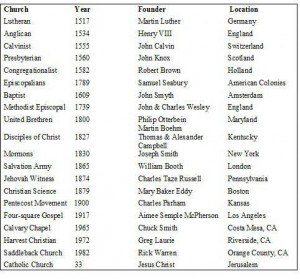
 We liturgically recall the dedication of the The Church of the Most Holy Saviour, Rome, is the cathedral church of Western Christianity. It is the Pope’s proper church. Dom Prosper Granger’s word remind us of the importance of this center, this home for all Christians. Honoring this church reminds us that we are an incarnational religion, that Christ Jesus has entered into our history, established a holy city –the Church– and has left us the sacraments mediated through the proclamation of the Gospel, the priesthood and ecclesial life. The church is not merely a building but a vital community of faith, truth and peace. It is the enfleshment of Beauty on earth.
We liturgically recall the dedication of the The Church of the Most Holy Saviour, Rome, is the cathedral church of Western Christianity. It is the Pope’s proper church. Dom Prosper Granger’s word remind us of the importance of this center, this home for all Christians. Honoring this church reminds us that we are an incarnational religion, that Christ Jesus has entered into our history, established a holy city –the Church– and has left us the sacraments mediated through the proclamation of the Gospel, the priesthood and ecclesial life. The church is not merely a building but a vital community of faith, truth and peace. It is the enfleshment of Beauty on earth.